The disease osteoarthritis has many variants.For example, a disease of the hip joint is called coxarthrosis and a disease of the knee is called gonarthrosis.
The treatment method is usually the same for all subtypes.However, many people do not know the difference between osteoarthritis and gonarthrosis of the knee joint.
Based on this, many incorrect uses of these terms have occurred among patients with this problem.
Causes
Gonarthrosis is a disease of the knee joint with damage to the cartilage tissue.Many people mistakenly believe that the disease is unique to older people because it is degenerative in nature.But as practice shows, gonarthrosis occurs more often in young people.
This is confirmed by the causes of the disease:
- Knee injuries (fractures, dislocations, tears);
- Weight lifting, intense physical activity without appropriate training;
- Inflammation of the joints due to the effects of various factors, including hypothermia;
- Excess weight, as it leads to severe stress on the joints and their subsequent degeneration;
- genetic predisposition.
As you can see, all factors for the occurrence of gonarthrosis are more typical in young people, since they lead an active lifestyle.
However, the disease can also occur in pensioners due to obesity.According to statistics, gonarthrosis occurs more often in women after 50 years.This is due to the restructuring of the body and changes in metabolic processes.
Principles and types of treatment
Since osteoarthritis is generally a chronic disease, treatment takes a long time.Therapy can be surgical or conservative.
In both the first and second methods, doctors try to somehow influence the cause of the disease and eliminate pathological symptoms.
It should be noted that surgical interventions are more typical for stages 3-4 of osteoarthritis.In the fourth case it is inevitable, and in the third case you can still try to overcome the disease using conservative methods.
In addition, it is recommended to use special gymnastic exercises, for example, the Bubnovsky technique.
In addition to the destruction of cartilage caused by gonarthrosis, muscle fibers and ligaments are also susceptible to destruction.The aim of the treatment is:
- relief from pain;
- elimination of inflammation;
- removal of edema in the periarticular area;
- Stopping the destruction of cartilage, its complete or partial restoration;
- Return to a fulfilling life and freedom of movement.
Even if osteoarthritis of the knee joint cannot be completely cured, a partial return to a normal lifestyle can be achieved through therapy and prevention.The condition persists until the next relapse.
Conservative method
This method of therapy is used in most cases and is the most important.As a rule, patients in the early and middle stages of gonarthrosis are treated in this way.All measures use medications (tablets, capsules, injections) with chemically active substances.
The following can be prescribed for treatment:
- analgin;
- chondroprotectors;
- non-steroidal drugs;
- synovial prostheses;
- Glucocorticosteroids.
Other conservative methods include treatment with various ointments, mud baths, etc.
Recently, gymnastics and light physical exercise have become very popular to stop the progression of the disease or possible recovery of the patient.
The body reacts strongly to non-steroidal drugs.Nevertheless, they are often used in the treatment of osteoarthritis due to their multifunctional effect:
- elimination of swelling in the joint;
- relief from pain;
- Treatment of inflammatory processes.
Because of these properties, doctors are increasingly preferring these drugs over traditional analgesics.
Glucocorticosteroids are synthetic drugs that can replace the natural hormones produced by the adrenal glands.If we compare them with non-steroidal drugs, glucocorticosteroids are much stronger.In addition, they have an anti-allergic effect.
Chondroprotectors act directly on the cartilage and are a completely safe treatment for knee osteoarthritis (gonarthrosis).They are obtained from the bone structure of animals, fish cartilage and crustacean shells.The drugs are a building material for cartilage, they improve metabolic processes and proper nutrition of the joint.
In addition to taking medications, the following are prescribed during treatment, recovery and prevention:
- physiotherapy;
- physiotherapy;
- various massages;
- Visiting sanatoriums and resorts.

All this allows the patient to return to normal life and corrects the result achieved with conservative treatment.
Furthermore, the courses are easy.A very useful exercise for the knee joint for gonarthrosis is to roll a ball or other cylindrical object placed on the floor, such as a rolling pin, with your foot.
Surgical intervention
If it is not possible to cure the disease with the help of medication or therapeutic exercises, surgery is required.This can be done on both open and closed joints.At the same time, surgical methods are being improved every day and new methods are being added to the previous ones, which are performed using modern equipment.
New methods of performing operations include:
- microsurgical intervention to restore damaged cartilage tissue;
- Treatment with a laser beam with the required characteristics – thickness, power, etc.;
- Creation of a 1 mm thick electrolytic plasma field;
- arthroscopy;
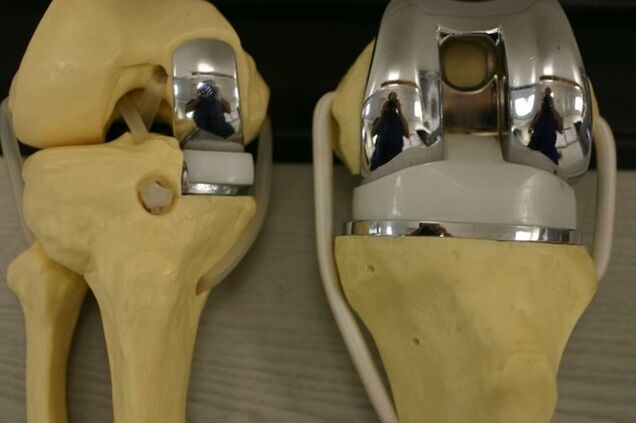
- Endoprosthetics – replacement of joint parts with artificial prostheses.
Modern surgical methods are less traumatic and enable a variety of different manipulations of the joint.
Traditional medicine recipes
Conservative treatment methods cannot always provide the maximum result in the treatment of gonarthrosis.Traditional medicine recipes can be used as additional remedies.
To get rid of knee pain and crunching, you can use the following recipe:
- 150 g garlic;
- 4 lemons with peel;
- 250 g celery roots.
Grind all components in a meat grinder, mix and pour boiling water over them.Then put it in a pot, close it tightly with a lid and let it cool.Take 60-70 g three times a day for a month.If pain occurs, you can repeat the course for prevention or do it every six months.
You can also use this recipe:
- Beat two eggs and mix with 4 tablespoons salt;
- Apply the mixture to a bandage and apply to the sore spot.
The process must be repeated twice in a row.Do not remove the bandage until the mixture has dried.
To make a medicinal ointment you will need the following ingredients:
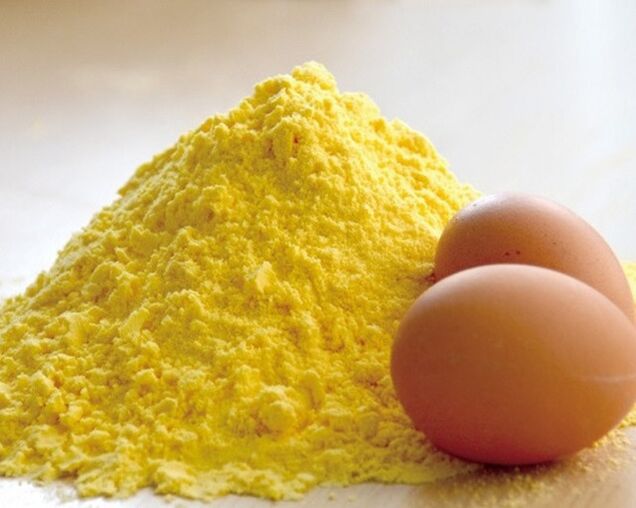

- 200 g of alcohol;
- 4 egg whites;
- 50 g camphor;
- 50 g mustard powder.
Add mustard and camphor alternately to the alcohol.Beat the egg whites in another container and then mix them together.The ointment is applied to the sore spot.
Of course, vigorous physical activity in athletes is just as common a cause of gonarthrosis as aging of the joints over time.
However, recently it has become increasingly common for the condition to occur without such underlying causes.In contrast, people lead a sedentary lifestyle, which is why they gain extra pounds.
The strain on the joints increases and prevents them from remaining healthy for a long time.
The difference between osteoarthritis and gonarthrosis
Not everyone understands the difference between gonarthrosis and arthrosis of the knee joint.Gonarthrosis is characterized only by damage to the knee, while osteoarthritis itself is the name for a group of joint diseases that can affect any joint.
In the theory of medicine there are many diseases whose names contain the part “arthrosis” - osteoarthrosis, polyarthrosis, coxarthrosis, gonarthrosis.In this regard, ignorant people do not always correctly understand the meaning of each term and think that they are all synonyms.
Gonarthrosis can easily be confused with the following diseases:
- Arthritis;
- vascular pain in the knees;
- Periarthritis – inflammation of the hamstrings;
- Meniscus damage.
Nevertheless, it is possible to differentiate gonarthrosis from these diseases.For example, meniscus damage (meniscopathy) is a disease that begins with sharp and unexpected pain in the knees after unsuccessful movement and over the years develops and progresses into gonarthrosis.If meniscopathy is left untreated, pain may occasionally occur but bone deformation does not occur.
With coxarthrosis (disease of the hip joint), reflex pain in the knees often occurs, but the two diseases can be distinguished from each other as follows:
- with gonarthrosis, a person can calmly move and spread his legs at the hip joint;
- With coxarthrosis, on the other hand, the patient can freely bend and straighten the knee;
- If pain occurs in both joints, it can be assumed that you have polyarthrosis.
Arthritis is characterized by sudden inflammation of the joints, but the pain does not affect the mobility of the joints (as in periarthritis) and is eliminated by warming ointments.This disease causes swelling, high fever, and increased pain at night.
Vascular pain occurs due to circulatory disorders - this often affects young people under the age of 20.This is due to the rapid growth of the entire organism.
Therefore, osteoarthritis is the general name of the disease, and gonarthrosis is a name indicating the location (knee).Therefore, it is correct to say either “arthrosis of the knee joint” or “gonarthrosis”, but not “gonarthrosis of the knee joint”.And it is entirely possible to make an accurate diagnosis through careful research and personal observations.
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint (gonarthrosis): diagnosis and treatment
The knee joint is a wonderful flexion and extension mechanism that nature has provided us with.At rest, it occurs only in disabled people and excessively obese people who have lost the ability to move.
Count how many times a day he makes movements and you will come to the conclusion that the knee is the most mobile part of the joint.It's no wonder that illnesses often target it.
One of them is gonarthrosis or osteoarthritis of the knee joint.
Causes of osteoarthritis of the knee joint
It's hard to say what causes early cartilage deficiency in some people.It is generally believed that a metabolic disorder is to blame, in which the metabolism of amino acids and important trace elements is slow or faulty.
Here again the following reasons are to blame:
- Some immune-related diseases (e.g. rheumatoid arthritis)
- A disregard for oneself: Sport and exercise, a complete diet with all vitamins, amino acids and minerals are often pushed aside by people who are far away for “later” (“I’ll start on Monday, of course”).
- The natural balance is disturbed right from birth - so-called hereditary causes.It's easy to check your genetic makeup: look at what your grandparents got sick with and ask them what their ancestors got sick with
- Disturbed hormonal balance: Such disorders particularly affect the female body during a phase of estrogen deficiency, an important hormone that is necessary for osteosynthesis.It is not for nothing that most of the victims of arthrosis are women of a wonderfully mature age, when they are not yet old, but already wise, i.e. the mark “over 50”.
- Vascular diseases: Osteoarthritis is often accompanied by venous insufficiency, venous thrombosis and other diseases
- Mood: If you think that stress only spoils your mood, you are wrong - stress can slow down your metabolism and put you in a state of restlessness
- A risk factor for osteoarthritis is too much weight
What symptoms suggest this terrible pathology?
Symptoms of gonarthrosis by stage
Each stage has its own peculiarities, which, however, are united by the gradual development of the disease:
You can't suddenly stop walking because of pain: A sharp, sudden pain in the knee most likely indicates an injury.
First stage.In the first stage the following symptoms appear:
- Mild pain after a long walk, climbing stairs, etc.
- Stiffness after rest
- The knee does not present any deformity, but it may be slightly swollen due to the accumulation of fluid: this phenomenon is called synovitis.Fluid can even collect in the back of the knee, forming a cyst that is often mistaken for a cancerous tumor by frightened patients.The cyst usually disappears easily after treatment with injections of NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) or glucocorticosteroids
Second stage
At the second stage, the following signs are noted:
- Increased pain after training and exercise and the appearance of a characteristic rough crunch
- Increasing morning stiffness
- Movement the entire way or even 90 degrees is accompanied by a pain symptom that is sometimes so severe that it becomes impossible to complete it
- As the deformation begins, the bones thicken and become rough - this can be determined by palpation
- Synovitis can get worse
Third stage
In the third stage, which is already defined as late deforming arthrosis of the knee joint, the following symptoms appear:
- Constant pain that doesn't go away even at night: The knee hurts and twists, especially in cold, damp weather
- A sharp reduction in the range of motion: no more than 90 degrees or even less
- Changes in gait: The patient begins to limp, walks slowly on half-bent legs, waddles, and has particular difficulty climbing stairs
- Visible severe deformation with mixing of the joint axes - as a result, the legs take the shape of the letter “X” or “O” (such signs are called hallux valgus).
- At this stage, the cartilage is usually completely destroyed and ossification (ossification) of the ligaments occurs.
- As a result, the joint surface becomes overgrown with calcium deposits, giving the knee a lumpy, uneven appearance.
- Due to the severe deformation and lack of synovial fluid, movements in the knee become extremely painful
- Gradually, the knee joint becomes almost completely immobile - late deforming arthrosis of the knee joint
Treatment of gonarthrosis
The treatment of this disease is complex and lengthy and is effective only in the initial stages.In the latter case, conservative treatment only helps to alleviate the patient's situation.
diagnosis.An important preliminary stage is diagnosis.
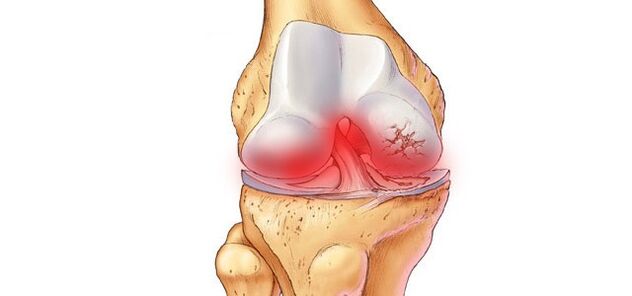
- The best way to diagnose and determine whether the pain is caused by an injury or osteoarthritis is to have an X-ray or MRI scan of the knee joint.
- Osteoarthritis is diagnosed when the following are detected: degeneration or absence of cartilage tissue and a small gap between the joint and the capsule
Conservative treatment
In case of exacerbations, the most important treatment condition is:
- Maintain rest and light exercise
- Taking painkillers (for severe pain – in the form of intra-articular injections)
- In the third and fourth stages of osteoarthritis, additional injections of fluid are prescribed to lubricate the joints
The following types of physiotherapy are effective for gonarthrosis:
- SWT (shock wave therapy)
- Electromyostimulation
- acupuncture
- Magnetic field therapy
- radiofrequency therapy etc.
Rehabilitation treatment
In order to avoid contractures and even greater immobility, knee exercises should be started immediately after the acute pain has subsided - for this exercise therapy is prescribed under the supervision of a rehabilitation specialist.Long-term cyclic administration of substitutes for natural components of cartilage - chondroprotective drugs - is also carried out.
Danger: In the third degree, arthrosis of the knee joint cannot be cured with the help of chondroprotectors.
Surgical treatment
Effective treatment of late arthrosis is only surgical intervention - the replacement of a dysfunctional joint with an endoprosthesis.
However, we must remember:
- As you get older, the healing of the prosthesis is slower
- You may experience pain for a year after surgery
- Long-term rehabilitation with mechanotherapy and comprehensive exercise therapy is required
If the patient refuses surgery, conservative supportive treatment is prescribed, the aim of which is to control pain and preserve the motor function of the knee
What is osteoarthritis of the knee joint often confused with – gonarthrosis?
- When diagnosing gonarthrosisErrors are just as common, if not more common, than in diagnosing hip disorders.
- Below you will find a list of the diseases that are most often confused with osteoarthritis of the knee joint (gonarthrosis).
- From the practice of Dr.Evdokimenko,Most often, arthrosis of the knee joint is confused with the following diseases:
Damage to the menisci (meniscopathy) and blockage of the knee joint
Meniscus injuries and knee locks occur in people of all ages, young and old.Men and women get sick at the same rate.Usually a knee joint is damaged.
In contrast to gonarthrosis, the disease develops quickly.As a rule, after an unsuccessful movement while walking, running or jumping, you hear a crunch in the knee and feel acute pain in the joint.After 10-15 minutes, the acute pain subsides slightly and the person can move.But the next day or the next, the knee swells and the pain intensifies again.
Without proper treatment, the disease lasts for years - the pain either subsides or recurs.However, compared to gonarthrosis, meniscopathy rarely causes deformation of the bones of the knee joint - unless damage to the meniscus triggers the development of knee osteoarthritis.And it should be noted that this happens quite often.
Osteoarthritis of the hip joint (coxarthrosis)
The diagnosis of “gonarthrosis” is often incorrectly made with “referred” pain, which often occurs with osteoarthritis of the hip joint and extends from the hip joint to the knee.
But these conditions are very easy to distinguish - with arthrosis of the hip joint, the mobility of the knee does not decrease at all, the knee can be bent and straightened easily and painlessly.
But the ability of a person suffering from arthrosis of the hip joint to turn the leg “from the hip” and spread the legs to the sides decreases sharply.
In contrast, a person suffering from gonarthrosis rotates his leg slightly from the hip and spreads his legs slightly to the sides.But he only bends his knee with difficulty and squats down in pain.
arthritis
Knee joints are the most vulnerable joints in the human body.In addition to osteoarthritis and meniscopathy, the knee joints can be affected by any of the arthritis described in the second part of the book - reactive, rheumatoid, psoriatic, gout, ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Arthritis affects people of all ages, but the disease is most common in young people.
With arthritis, one or both knees can become inflamed.
A characteristic feature of arthritic inflammation of the knee joint is a rapid onset (within 1-3 days) with significant swelling and swelling of the knee and increased pain in the affected joint at night (around 3-4 a.m.).This means that the pain may be more severe at night when resting than when walking.As you remember, pain in arthrosis decreases at night.
In addition, almost all arthritis leads to inflammation of not one but several joints at the same time: In addition to the knee joints, the finger and toe joints, elbow joints, ankle joints and heel tendons also become inflamed and swollen in any combination.
Vascular pain in the knees
Many people are familiar with this pain, which is caused by poor blood circulation in the knee joints.They usually begin in adolescence, a period of active growth, as vascular development often does not keep pace with accelerated bone growth in rapidly growing adolescents.
Vascular pain in the knees that occurs once can accompany a person almost their entire life.However, their intensity usually decreases after 18-20 years (and does not increase with age, as is the case with osteoarthritis).And in contrast to osteoarthritis pain, vascular pain in the knees is not accompanied by a restriction in the mobility of the knee joints.
Pain sensations are usually symmetrical, that is, they are equally pronounced in the right and left knee;occur during changes in the weather, in cold weather, during colds and after physical activity.At such moments, suffering people complain that their knees “twist.”
In most cases, vascular pain in the knees can be easily eliminated by rubbing with warm ointments, massage and self-massage (vigorously rubbing the knees), or taking vasodilator medications.No special therapy is required for this disease.
Inflammation of the hamstrings (periarthritis of the anserine bursa)
Women are most often affected, most commonly over the age of 40.Pain usually occurs when climbing stairs or when carrying heavy objects or heavy bags.Pain is extremely rare when walking quietly on a flat surface.
The pain caused by periarthritis does not extend to the entire knee.The focus is solely on the inside of the knees, about 10 feet below the point where the knees would touch if you brought your legs together.And in contrast to osteoarthritis, periarthritis does not result in any restriction of knee mobility;The leg is fully flexed and extended at the knee as expected.


































